Abstract
Introduction: The Phase III Gallium study has shown that induction with the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody obinutuzumab (GA101; G) plus chemotherapy followed by maintenance with G alone significantly prolongs PFS relative to the corresponding rituximab-containing regimen in previously untreated pts with follicular lymphoma (FL). However, FL remains incurable, and most pts eventually relapse. Atezolizumab (atezo), which targets programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), has a complementary mechanism of action to G and has the potential to improve outcomes when added to G-chemotherapy in FL. We report interim data from a single FL cohort from our Phase Ib/II study (NCT02596971) of the safety and efficacy of induction with G-bendamustine (benda)-atezo followed by maintenance with G-atezo.
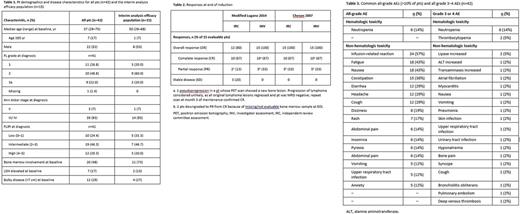
Methods: Pts (≥18 yrs old, ECOG PS 0-2) with FL (previously untreated grade 1, 2 or 3a disease requiring therapy or relapsed/refractory [R/R]) received induction with infusions of G 1000 mg on days 1, 8 and 15 of cycle 1 and day 1 of cycles 2-6, benda 90 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 of cycles 1-6, and atezo 840 mg on days 1 and 15 of cycles 2-6 (28-day cycles). Maintenance in pts with CR or PR consisted of G 1000 mg on day 1 of every other month and atezo 840 mg on days 1 and 2 of each month for ≤24 months. Enrollment included an initial safety run-in phase with intensive safety monitoring in 6 pts before the main enrolment (expansion phase) began; R/R pts were permitted in the safety run-in phase only. The primary endpoint was CR (PET-CT) rate at end of induction (EOI) determined by independent review committee (IRC) using modified Lugano 2014 criteria. Secondary endpoints included CR rate at EOI assessed by investigator (INV) using modified Lugano 2014, CR rate at EOI by IRC and INV using modified Cheson 2007, ORR at EOI by IRC and INV using modified Lugano 2014 and modified Cheson 2007, DoR, and PFS and EFS by INV. MRD as an exploratory endpoint was centrally assessed by next generation sequencing of the B-cell receptor VDJ region in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Safety and tolerability were also assessed. This interim analysis was performed after the first 15 pts with previously untreated FL had completed induction or discontinued beforehand (interim analysis efficacy population). The data cut-off for the analysis was March 7, 2017.
Results: In total, 42 pts (including 40 with previously untreated FL) were enrolled and treated. At the time of data cut-off, 22 were still in induction, 3 had discontinued because of AEs, 17 had completed induction, and 15 were receiving maintenance. Pt demographics and disease characteristics are shown in Table 1. CR rates (IRC and INV) were 67% (n=10/15) by modified Lugano 2014 and Cheson 2007 criteria (Table2). Most pts received >95% of the planned doses of G, benda and atezo during induction. The median dose intensity for all three drugs was 100%, with means of 95.1% to 99.2%. All pts had ≥1 AE, 20 (48%) had a grade 3-4 AE, and 1 had a grade 5 (fatal) AE (unrelated sudden death). A second grade 5 AE (atezo-related cardiac arrest) was reported after the data cut-off in a pt with grade 4 myocarditis and bronchiolitis obliterans (likely immune-mediated AEs) in whom the cardiac arrest was preceded by a dyspnea event. Nine pts (21%) had SAEs. AEs led to dose reduction (benda only) in 4 (10%) pts (grade 4 neutropenia, grade 2 diarrhea, two grade 3 transaminase increases) and to withdrawal of at least one treatment in 4 (10%) pts (grade 4 myocarditis in the pt with cardiac arrest after data cut-off, grade 3 lipase increase, grade 3 cough, grade 3 pneumonia); 22 (52%) pts had AEs requiring interruption of any treatment. The most common hematologic toxicity was neutropenia; other frequent toxicities were infusion-related reactions (IRRs), fatigue and gastrointestinal events (Table3). The most common treatment-related grade 3-4 toxicities were neutropenia (6 pts [14%], 3 of whom received G-CSF prophylaxis) and thrombocytopenia (2, 5%). The most frequent treatment-related SAE was IRR (2 [5%], both atezo-related).
Conclusions: In this interim analysis of the G-benda-atezo combination, one treatment-related death occurred. Toxicity was otherwise manageable. Preliminary efficacy data show encouraging first-line activity in FL. Results from the final analysis based on 40 pts, including DoR, PFS and EFS, will be presented at the meeting.
Younes: Sanofi: Honoraria; Curis: Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria; Takeda Millenium: Honoraria; Incyte: Honoraria; Johnson & Johnson: Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Third-party medical writing assistance, under the direction of Anas Younes, was provided by Scott Malkin of Gardiner-Caldwell Communications, and was funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; Merck: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Novartis: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Seattle Genetics: Honoraria; Bayer: Honoraria. John: Incyte: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy. Diefenbach: Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Kahn: Roche: Honoraria. Sharman: Novartis: Research Funding; Gilead Sciences, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Genentech: Research Funding. Ujjani: Gilead: Consultancy; Abbvie: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Genentech: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding. Vitolo: Takeda: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Mundipharma: Honoraria. Woodard: Genentech, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Mundt: Roche: Employment. Fingerle-Rowson: F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Employment, Equity Ownership. Chitra: Genentech: Employment. Sellam: Roche: Employment. Morariu-Zamfir: Roche: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal